Describe the Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action
Only the correctly sized key substrate fits into the key hole active site of the lock enzyme. Lock and Key Model.
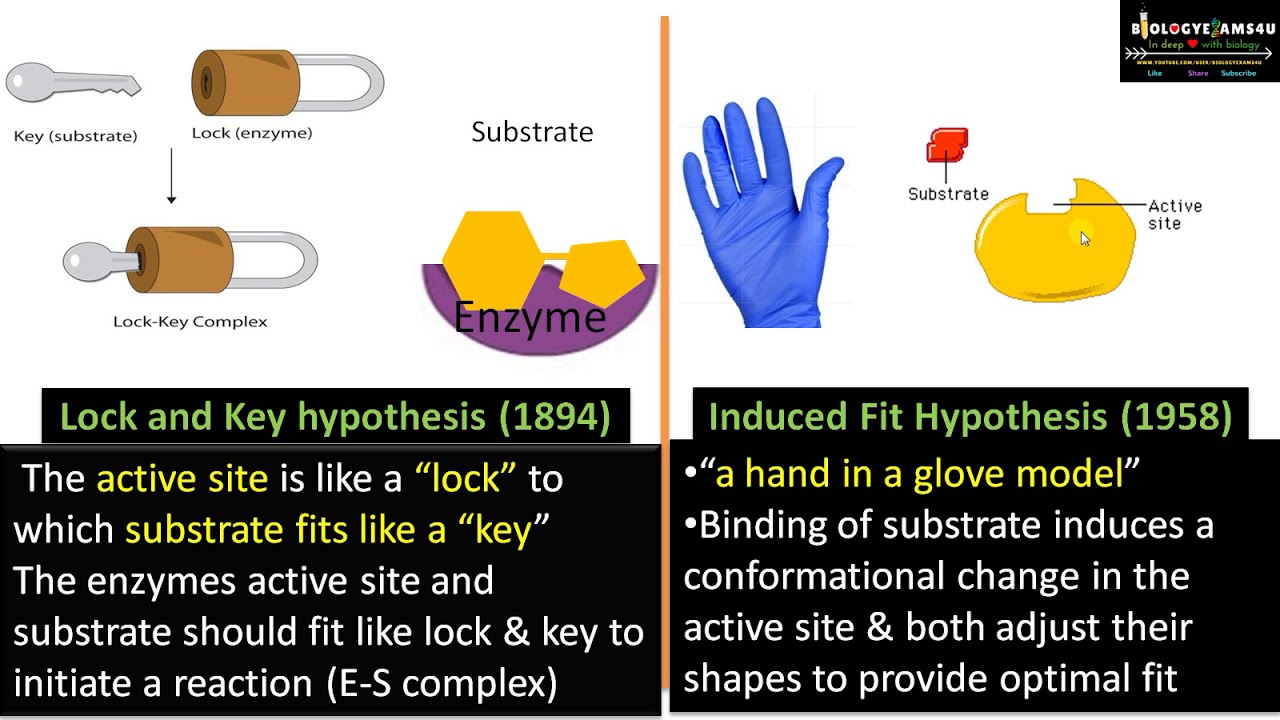
Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Biology Notes Lock And Key
Fischer has developed a Lock and Key theory to describe the mode of action of the enzyme.

. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. What does the enzyme action form. Similar to how a key has to be the correct one for a lock no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind.
In this analogy the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate. An enzyme is a protein that functions as a biological catalyst by speeding up chemical reactions and remaining unchanged by the reaction. These enzyme molecules can only be opened with the help of specific substrate complexes.
Induced fit and lock and key are the two models which describe the mechanism of action of the enzyme. When the enzyme locates its appropriate substrate the substrate enters the receptor site and both the enzyme and substrate transform to create a complete union so the chemical reaction can occur. View the full answer.
The lock and key model also called Fishers theory is one of two models which describe the enzyme-substrate interaction. Likewise if the right enzyme fits into the right substrate the drug will form otherwise it wont. It possesses a unique shape that complements that of the substrate.
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100 3 ratings Question 23 According to the lock and key model enzyme and substrate molecule are complementary in their shape that help them to bind with each other and therefore help in the catalysis by an enzyme. The substrate and enzyme complement each other. Click on the mouse at left to clear the images and text.
An enzyme substrate complex. The place on an enzyme where the molecule binds is called the active site. In this case the molecule completes with the substrate and the reaction may either slow down or stop.
Only the correctly sized key substrate fits into the key hole active site of the lock enzyme. This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able. The specific action of an enzyme with a single substrate can be explained using a Lock and Key analogy first postulated in 1894 by Emil Fischer.
The enzyme is like a lock and substrate is like. What is the lock-and-key model of enzyme action. Figure 1811 The Lock-and-Key Model of Enzyme Action.
Explain the lock and key model. Both models depend on the degree of precise binding of the substrate to the active site of the enzyme. In the lock and key model the shape of the active site exactly matches the shape of the substrate.
What happens if you heat the enzyme. Emil Fischer proposed this model in 1894. The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate.
The key substrate has a specific shape arrangement of functional groups and other atoms that allows it and no other key to fit into the lock the enzyme. Click on the numbers below to see how the lock-and-key model of enzyme action works. The enzyme and substrate fit like a lock and key and thus is a lock and key model of enzyme action.
Similarities Between Induced Fit and Lock and Key Model. Just as the lock and key model this hypothesis states that the active sites of enzymes act as a lock that has specific molecules such as -COOH and -SH. These enzyme molecules can only be opened with the help of specific substrate complexes.
This modified lock and key model known as the induced fit theory also explains why some substrates known as inhibitors fit in the enzyme site but. Lock and key model Enzymes are. According to this principle if the right key fits inside the right lock the lock will be opened otherwise it will not.
They are important in describing how enzymes increase the rate of a biological reaction through. Lock and Key Model The Lock and Key model is a theory of enzyme action hypothesized by Emil Fischer in 1899. In fact an early model describing the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex was called the lock-and-key model A model that portrays an enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to a substrate or substrates that exactly fit the active site.
View Answer Discussion You must be signed in to discuss. The Lock and Key and Induced Fit are theoretical models of enzyme activity that describe the enzymes recognition of substrates. Lock and Key Theory.
The active site of the enzyme denatures so the substrate can no longer fit it. According to this model. This model supports that a specific substratekey can be inserted into a particular enzymelock.
This hypothesis explains the specificity of enzymes and also the mode of action of enzymes. However sometimes other molecules which are similar to the substrate can also combine with the active site of an enzyme. The shape of the substrate fits the shape of the enzymes active site like a key fits a lock.
Then the general concept of the lock and key model should be explained to ensure that the student understandsThen the answer to the question should be written taking into account the number of marks that is available as this indicates how long the answer should beANSWERIn this model the key represents the enzyme and the lock represents the substrateThe lock and. The specific action of an enzyme with a single substrate can be explained using a Lock and Key analogy first postulated in 1894 by Emil Fischer. Learn more about enzymes and how they work and discover the.
The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the. Answer According to the lock and key model the shape of an active site on the surface of enzyme is just complementary to the shape of the substrate. An enzyme substrate complex.
Means that enzyme are subtrate-specific. An enzyme is a protein that functions as a biological catalyst a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction. In this analogy the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate.
The active site of an enzyme is a specific region that receives the substrate. Watch More Solved Questions in Chapter 20 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5. In this analogy the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate.
As one specific key can open only a specific lock just like that a specific enzyme can convert only one particular substrate into. According to Fischer enzymes exhibit a high degree of specificity to the substances. The lock-and-key model refers to the way in which a substrate binds to an enzymes active site.

Lock And Key Model A Model For Enzyme Action Enzymes Biology Enzymes What Is A Product

Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Biology Notes Lock And Key

What Is The Correct Model For Enzyme Substrate Complementarity Active Site Biochemistry Teaching Biology
No comments for "Describe the Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action"
Post a Comment